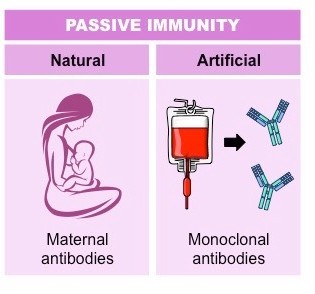
Occurs when active antibodies are given to someone that cannot produce their own antibodies.
Given through:
- A mother's antibodies passing through the placenta to the baby
- Through antibody-containing blood products (monoclonal antibodies)
- Given when immediate protection from a specific disease is needed
Protection is immediate, but only lasts for a few weeks or months.
Natural Immunity
Occurs when a person is exposed to a live pathogen and produces antibodies in response.
Given through:
- Direct contact with pathogen
Protection is adapted, but long-lasting.
Pathogens are in larger doses when infected naturally, this means better immunity, but also increased effects of symptoms.
Risks that come with natural immunity
- Pneumonia from Chickenpox
- Intellectual disability from Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib)
- Pneumonia from Pneumococcus
- Birth defects from Rubella
- Liver cancer from Hepatitis B virus
- Death from Measles
All of these can be prevented by getting vaccinated!

Comments
Post a Comment